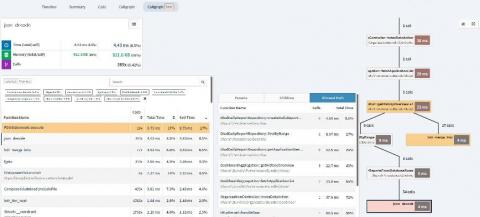
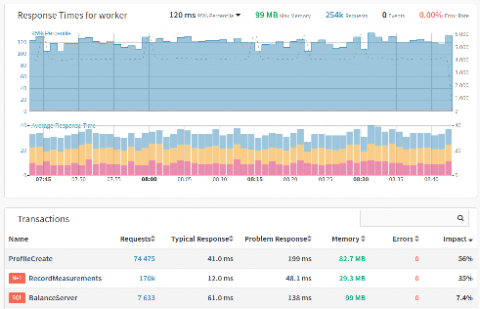
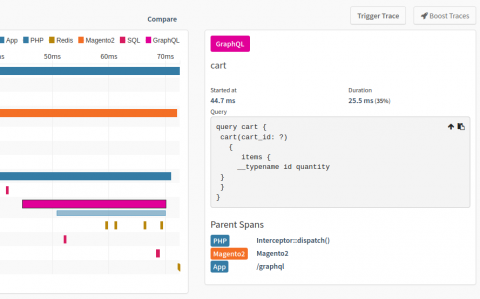
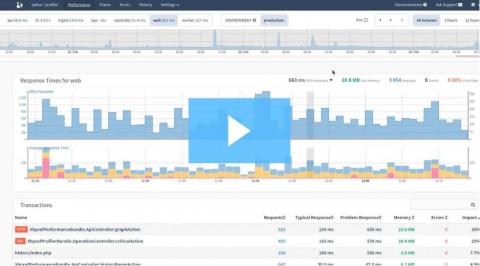
Spring Release: Tracepoints, Callgraphs, Slow SQL Log and Deprecations
We are releasing a new stable minor version of the Tideways PHP extension 5.1 today, which will include a few new features that we have been writing about before and a few new ones that we have cooked up in the last few weeks.