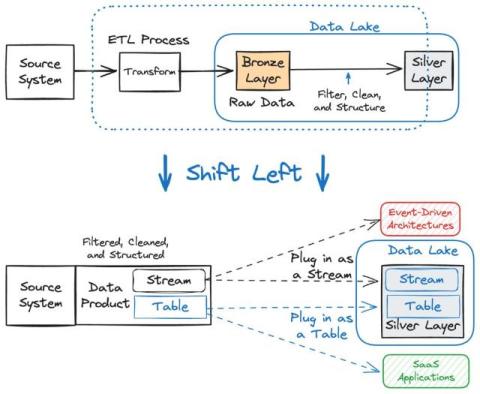
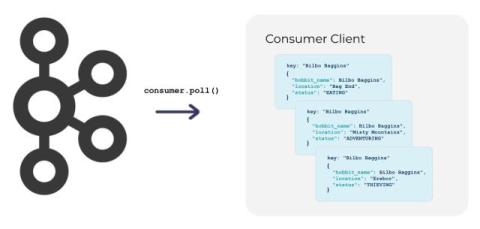
How to Visualize Real-Time Data from Apache Kafka using Apache Flink SQL and Streamlit
Data visualization is cool, but have you tried setting up a chart of real-time data? In this video, Lucia Cerchie shows you how to create a live visualization of market data. She starts by producing data to a topic in Confluent Cloud from an Alpaca API websocket, then processes that data with Flink SQL, and finally uses a Streamlit component for a real-time visualization.