Guide to Parallel Processing in Python
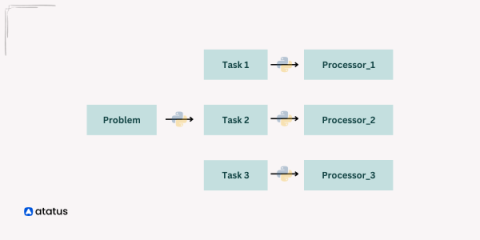
Parallel processing in computers is like having an efficient team working on different parts of a task simultaneously. In traditional programming, tasks are executed one after the other, like solving a puzzle piece by piece. However, parallel processing divides the task into smaller chunks, and these chunks are handled simultaneously by multiple processors or cores. Python provides modules that allow programs to leverage multiple processor cores efficiently.