Systems | Development | Analytics | API | Testing
%term
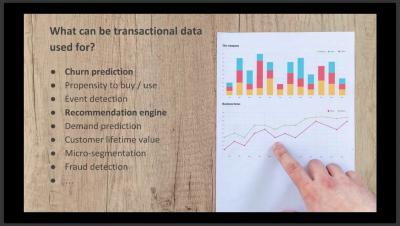
Webinar: Introduction to Transactional Data
Shift Left: The Art of Continuous Monitoring
Legacy Versus Next-Generation - How Open Source is Driving the Big Data Market
When it comes to solutions for the big data sector, there is a clear split between the legacy and next-generation approaches to software development. Legacy vendors in this space generally have their own large internal development organizations, dedicated to building proprietary, bespoke software. It’s an approach that has worked well over the years.
What is Cloud-Native? Is It Hype or The Future of Software Development?
For quite a while now, cloud-native has been one of the hottest topics in software development. Some developers just call it hype that will lose traction and disappear after some time. For others, it’s the future of software development. Whatever the future will bring, cloud-native is currently one of the biggest trends in the software industry. It has already changed the way we think about developing, deploying and operating software products. But what exactly is “cloud native”?
Talend Step-by-Step: Continuous Data Matching & Machine Learning with Microsoft Azure
Today, almost everyone has big data, machine learning and cloud at the top of their IT “to-do” list. The importance of these technologies can’t be overemphasized as all three are opening up innovation, uncovering opportunities and optimizing businesses. Machine learning isn’t a brand new concept, simple machine learning algorithms actually date back to the 1950s, though today it’s subject to large-scale data sets and applications.
How to process weather satellite data in real-time in BigQuery
Since the 1960s, scientists have been forecasting the weather using satellite-captured imagery. Although access to these satellite feeds used to be reserved just for meteorologists, these days anyone can jump online to find current satellite footage for their area. But what if you wanted to take things a step further? Maybe you’re curious about the history of weather events, or want to create a real-time feed for where you live.
The future of DevOps is mastery of multi-cloud environments
DevOps is a set of practices that automates the processes between software development and IT teams so they can build, test, and release software more quickly and reliably. The concept of DevOps is founded on building a culture of collaboration between IT and business teams, which have historically functioned in relative siloes. The promised benefits include increased trust, faster software releases, and the ability to solve critical issues quickly.